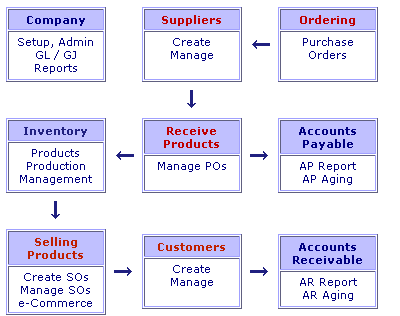

The Navigator is like a high-level block diagram of the program. It is provided to help the beginner understand the flow and make it easy to locate the various functions. The Navigator toggles with the Main Menu, which provides access to all functions in the program.
1. "Company"
As in any accounting program, you must define a Chart of Accounts and setup a company name and preferences for your company, before proceeding with any transactions. Select “Company” then “crate new” if you need to create a new account. The system comes with a standard chart applicable to most situations. To make changes to account descriptions click on the account name link at the outset before balances are posted to the accounts. To enter company name and other relevant information click on the “Admin” link within “Company” block2. “Inventory”
Inventory
records are prerequisite for creating purchase orders and sales orders. Select
the title of this block or the “products” entry, within it to create a new
product. Product is defined as any
component assembly or service. They all must be created here first. Assemblies
have A or F as their category ID. You can define structures (BOM) for
Assemblies only, under “production management”. You can make changes to
description and other fields within all products under “manage” products by
selecting “Edit,
View, Delete”. You cannot delete a product with inventory quantity and/or if the product is part of an
assembly. To change the cost of a product you must go to “Physical Inventory”.
To “edit” a structure (delete an item from an assembly) go to “ create /edit
assemblies”.
3.
“Suppliers”
Supplier and inventory records are prerequisite to creating a purchase order. In
this block you create new suppliers and “Manage” make changes to existing. You
cannot delete a supplier with balances or open purchase orders.
Customer and inventory records are prerequisite to the creation of a sales
order. In this block you create new customers and “Manage” make changes to
existing. You cannot delete a customer with balances or open orders.
5.“Ordering”
After
the creation of inventory and supplier records go here to create an purchase
order. A purchase order can be cancelled and or modified under “Manage POs”
before the product is received.
6. “Receive Products”
Products ordered via PO are received into inventory. Once Received a PO cannot be
cancelled.
7. "Selling Products"
As in Suppliers you must have a customer and an inventory record to create a Sales order/Invoice. Click on the title of the block or on “Create SOs” to create a Sales order and an Invoice. A sales order cannot be canceled after it has been invoiced. The program provides for payment immediately after the invoice is created. If there is no payment the transaction will be added to the accounts receivable list. Payment can be received from “Manage” Sales orders” or from Accounts receivable “receive payment"
8.Accounts payableAfter
receiving a product the inventory is increased and an A/P record is created.
Click the title or on “A/P reports” to review. You can go to “Company’ and
invoke the “Transaction” file to see the transaction entries. Click
on “Make payments” to pay a Purchase order. Go
to “Company” “Checksbook” or “General Journal (G/J)” to pay
expenses which are not related to Purchase Orders.
9. Accounts receivable
Go
here to produce accounts receivable and aging reports. Also receive payments
from customers on outstanding invoices. Any other customer payment must be made
from the “check book” or General Journal.
Go
to "General Journal" to enter transactions. A helpful table is
displayed to assist those who are not very familiar with debits and credits.
1.
Depositing Money in the bank.
A
start up company deposits money from owners and investors into the bank. You
can use either the checkbook or the General Journal to accomplish this. In both
cases Debit the appropriate Bank and Credit an
equity account.
2. Paying Misc. Expenses.
To pay expenses again the checkbook
or the General Journal
3. Creating Purchase orders.
Go to the ordering block. To Manage purchase orders go to the “receive
products” block and click on Manage Pos.
4. Receiving Purchase orders.
You can receive a purchase order and make payment at he same time. If
you choose to make payment later, you can do from either “Manage POs “ or from
“Accounts payable “ “Make Payments”
5.
Paying Vendor invoices.
6. Creating Sales Orders / Managing Sales Orders,
go to the
“selling Products” block
7. Releasing Sales Orders / Creating Invoices. You can release an order immediately after creating a sales order, or you can do it later from “selling products” “Manage Sos”.
8. Receiving payments from customers. You can receive payment by selecting “yes” to the choice offered upon completion of the Invoice.. Or you can go to “Manage Sos” block or to “Accounts receivable “ block “Receive Payment”>9. Paying Miscellaneous Bills not Accounts Payable. .see above>
10. Making Journal entries. Go to “Company” block. And invoke the program. The program displays a table to help the novice with the Debits and Credits. Reviewing the General Ledger and Transaction file
III. System Administration
11. Backup and restore database.
I
V. Reporting